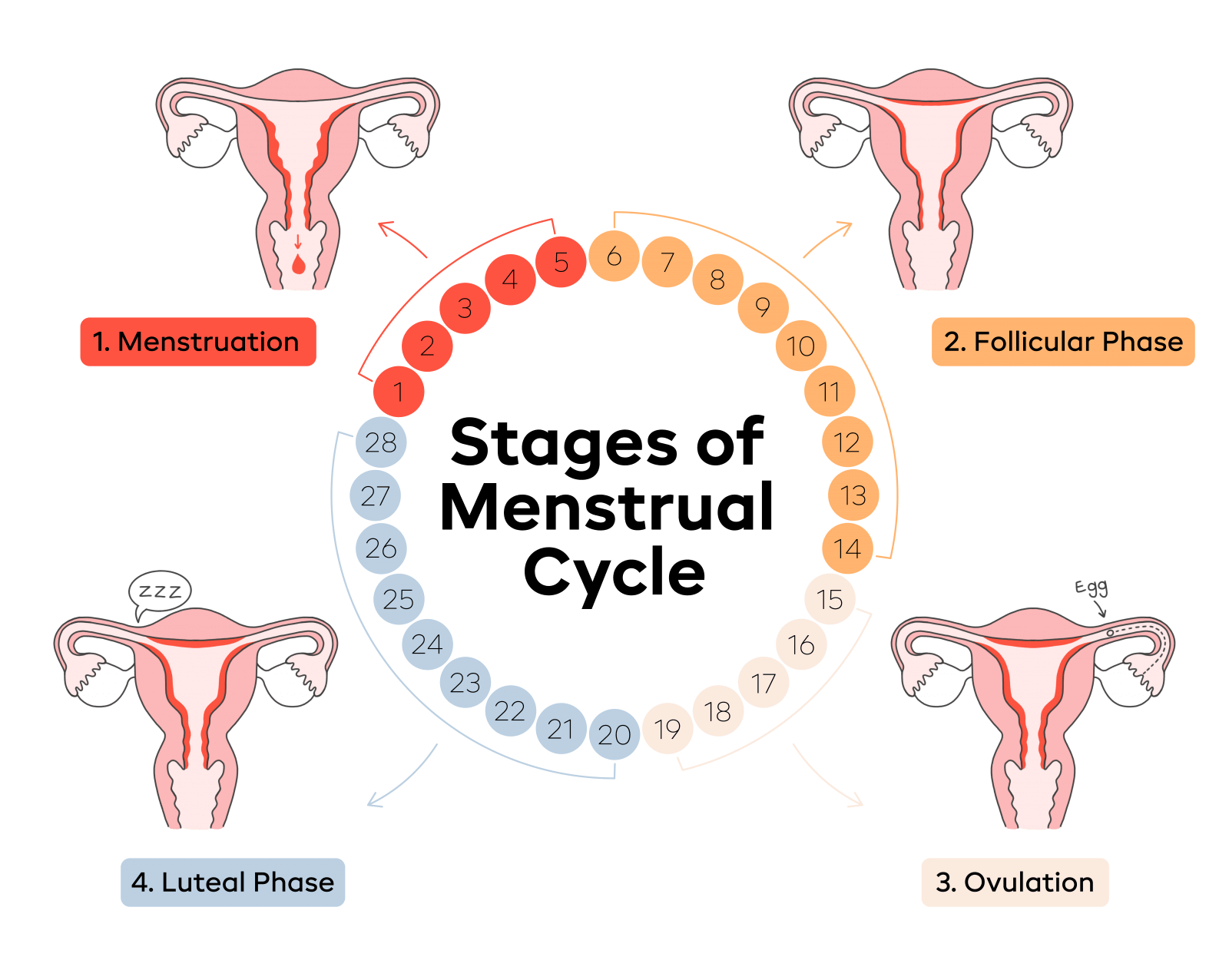
A woman’s body undergoes a variety of changes each month to prepare for a potential pregnancy. This series of hormone-influenced events is called the menstrual cycle.
The four stages of a woman’s menstrual cycle are as follows:
- Menstrual phase
- Follicular phase
- Ovulation phase
- Luteal phase
1. Menstrual Phase
The menstrual cycle’s first phase is at this point. This phase starts when an egg is not fertilized from the previous cycle, as pregnancy hasn’t taken place. This drops the levels of estrogen and progesterone. The thick lining of the uterus, which supports a pregnancy, is no longer needed, so it sheds through the vagina. During periods – there is a release of a combination of blood, mucus, and tissue from the uterus.
You may have period symptoms like these:
- Cramps
- Tender breasts
- Bloating
- Mood swings
- Irritability
- Headaches
- Tiredness
- Lower back pain
When a woman is menstruating, she typically goes between three to seven days. Some women’s periods are longer than others.
2. Follicular phase
On the first day of your period, the follicular phase begins and overlaps with the menstrual phase.
It starts when a signal is sent by the hypothalamus to your pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The ovaries are stimulated by this hormone to create 5 to 20 little sacs known as follicles. Each follicle contains an immature egg. Only the healthiest egg will mature. The remaining follicles will eventually be reabsorbed by the body.
The maturing follicle sets a surge for estrogen that thickens the lining of your uterus. This creates a nutrient-rich environment for an embryo to grow.
The follicular phase typically lasts 16 days. Depending on your cycle, it could last anywhere from 11 to 27 days.
3. Ovulation phase
The rising of estrogen levels during the follicular phase triggers your pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH). This starts the process of ovulation.
Your ovary produces a mature egg during ovulation. The egg travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus to be fertilized by sperm.
One can only get pregnant during the ovulation phase of the menstrual cycle. Signs of the ovulation phase include these symptoms:
- a slight rise in basal body temperature
- and thicker discharge that has the texture of egg whites
If you have a 28-day cycle, ovulation takes place around day 14 in the middle of your menstrual cycle. It lasts about 24 hours. If the egg is not fertilized within a day, it will disintegrate or expire.
4. Luteal phase
In the Luteal phase, the follicle transforms into the corpus luteum after releasing its egg. Progesterone and possibly estrogen are the major hormones released by this structure. The increase in hormones keeps the uterine lining thick and ready for the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Your body will generate human chorionic gonadotropin if you become pregnant (hCG). This is the hormone pregnancy test detects. It helps to preserve the corpus luteum and keeps the uterine lining thick. If you are unable to conceive, the corpus luteum will contract and resorb. This results in lower estrogen and progesterone levels, which trigger the start of your menstruation. The uterine lining will shed during your period.
If you don’t become pregnant during this phase, you can encounter premenstrual syndrome symptoms (PMS).
- bloating
- breast swelling, pain, or tenderness
- mood changes
- headache
- weight gain
- changes in sexual desire
- food cravings
- trouble sleeping
There are 11 to 17 days in the luteal phase. The average length is 14 days.
Identifying common issues-
Every woman’s menstrual cycle is different. Some women bleed for a longer period of time or with greater intensity than others. You may experience changes in your menstrual cycle from time to time. For instance, it might become increasingly erratic as you approach menopause.
Your menstrual cycle may change as a result of any of the following:
- Birth Control- This pill makes periods duration shorter and lighter in flow. While on some pills, one won’t get periods at all.
- Pregnancy- Missed periods are one of the most obvious first signs that you’re pregnant.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)- This hormonal imbalance prevents an egg from developing normally in the ovaries. PCOS causes irregular menstrual cycles and missed periods.
- Uterine Fibroids- These noncancerous growths in your uterus can make your periods longer and heavier than usual.
- Eating disorders- Anorexia, bulimia, and other eating disorders can disrupt your menstrual cycle and make your periods stop.
A few of the warning symptoms of an irregular menstrual cycle are as follows:
- You’ve skipped periods, or your periods have stopped entirely.
- Your periods are irregular.
- You bleed for more than seven days.
- Your periods are less than 21 days or more than 35 days apart.
- You bleed between periods (heavier than spotting).
Speak with your healthcare practitioner if you experience any of these or other issues with your menstrual cycle or periods.